em.jot.ge
finite.elements.and.more
Montag, 9. Januar 2012
Calculix 2.4 is out now!
The new version 2.4 of Calculix is released. For more information take a look here.
Donnerstag, 15. Dezember 2011
Freitag, 7. August 2009
bone.remodeling
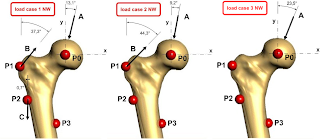
Proximal femur with initial stochastic density distribution under combined loading as depicted.
This leads to the following "remodeling" result:
For further information take a look at: "Finite Element Analysis of Bone Remodeling - Implementation of a Remodeling Algorithm in MATLAB and ANSYS

This leads to the following "remodeling" result:
For further information take a look at: "Finite Element Analysis of Bone Remodeling - Implementation of a Remodeling Algorithm in MATLAB and ANSYS
ansys.and.matlab.coupling
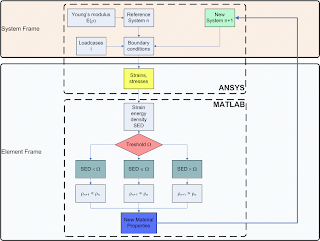
The algorithm depicted in this figure can be divided into the system frame and the element frame. In the system frame all input parameters are defined like geometry, material types, Young’s modulus and all boundary conditions. In the element frame the strain energy density is calculated per element, which acts as the stimulus. The threshold Ω shall be understood as the lazy zone. According to this threshold resorption, maintainance or formation occurs in the element, if the strain energy density is lower, within or greater than Ω, respectively. Due to this modification new material properties have to be defined leading to a new system.
The simulation is done using the commercial finite element software ANSYS®, version 9.0 and MATLAB®, version 6.1, whereas ANSYS takes the calculation part and MATLAB the control part including remodeling. The simulation is launched in MATLAB passing several parameters and the input file to ANSYS. The structural responses, such as strains and stresses are calculated and stored in arrays, like the material distribution. With the provided stresses and strains, MATLAB calculates the strain energy density and determinates whether remodeling occurs or not and modifies the material distribution. The next loop starts with the new configuration and continues until the simulation converges.
For further information take a look at:
Donnerstag, 16. Juli 2009
apple.impact
In this small FEM model both the apple and the leaf are under plane strain condition. The leaf is defined as rigid body and the apple as a hyperelasitc material. An initial velocity boundary condition is applied on the leaf. The simulation is done with explicit time integration in ABAQUS/explicit using the general contact feature. The normal surface behavior is defined as "hard" contact. This displacement magnitude is chosen as fringe result.
Abonnieren
Kommentare (Atom)